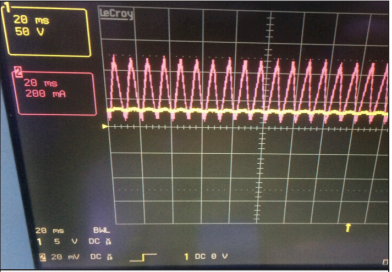
Although there are basic, constant-current, buck, boost, and buck–boost type light-emitting diode (LED) drivers in the market, new LED drivers are being proposed in the literature. Owing to the development of the LED technology, the control problems associated with LED drivers have also occurred. Not only the pure control of LED drivers, but also the isolation and power-factor correction (PFC) demands are challenge for engineers. In this study, snubber circuits are added to the PFC flyback LED drivers to analyze the system in detail. To that end, the `PAR230VEM application circuit is tested for its input and output parameters. The input and output waveforms of the PFC flyback LED driver are examined and compared with those of the other LED drivers in the literature. Subsequently, the proposed snubber circuits are added to the semiconductor components to improve the performance of the LED driver; this is because by adding the snubber circuits, the stress levels of the driver components are lowered. Consequently, the components with low stress levels improve the efficiency by approximately 9.4 %. Furthermore, the proposed isolated LED driver has unity power factor with 4.8 % THDi at the switching frequency of 69 kHz.
Cite this article as: Akın B. Snubber Circuit Application for Power-Factor Correction Flyback LED Driver. Electrica, 2020; 20(1): 108-116.



.png)

.png)